Many people associate rosacea with a chronic or recurrent inflammatory skin problem, because this is the most common form in which it manifests itself. However, few know that there is also a ocular rosaceawith analogous symptoms and treatments, substituting the conjunctiva for the skin.
Today we shall see What is ocular rosacea?, What are the possible causes?, What symptoms do you have? and what factors make them worse. Finally, we will review the ophthalmological treatments. When faced with a chronic condition, meaning that it can and often does recur, it is important to seek the help of a experienced ophthalmologistas the Dr. NebroTo explain to the patient how he/she needs to take care of the eyes and eyelids during acute episodes and how hygiene should be maintained between these episodes.
What is ocular rosacea?
The ocular rosacea is a chronic condition of the skin and eyes – specifically the conjunctiva – of an inflammatory nature. It seems to be more frequent in people who, in turn, have other skin diseases related to inflammatory processes and with a decrease in the defensive effectiveness of the natural barrier constituted by the skin and mucous membranes, as is the case of the psoriasis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Rosacea of the eyes can affect only the conjunctiva, only the eyelids, or both.
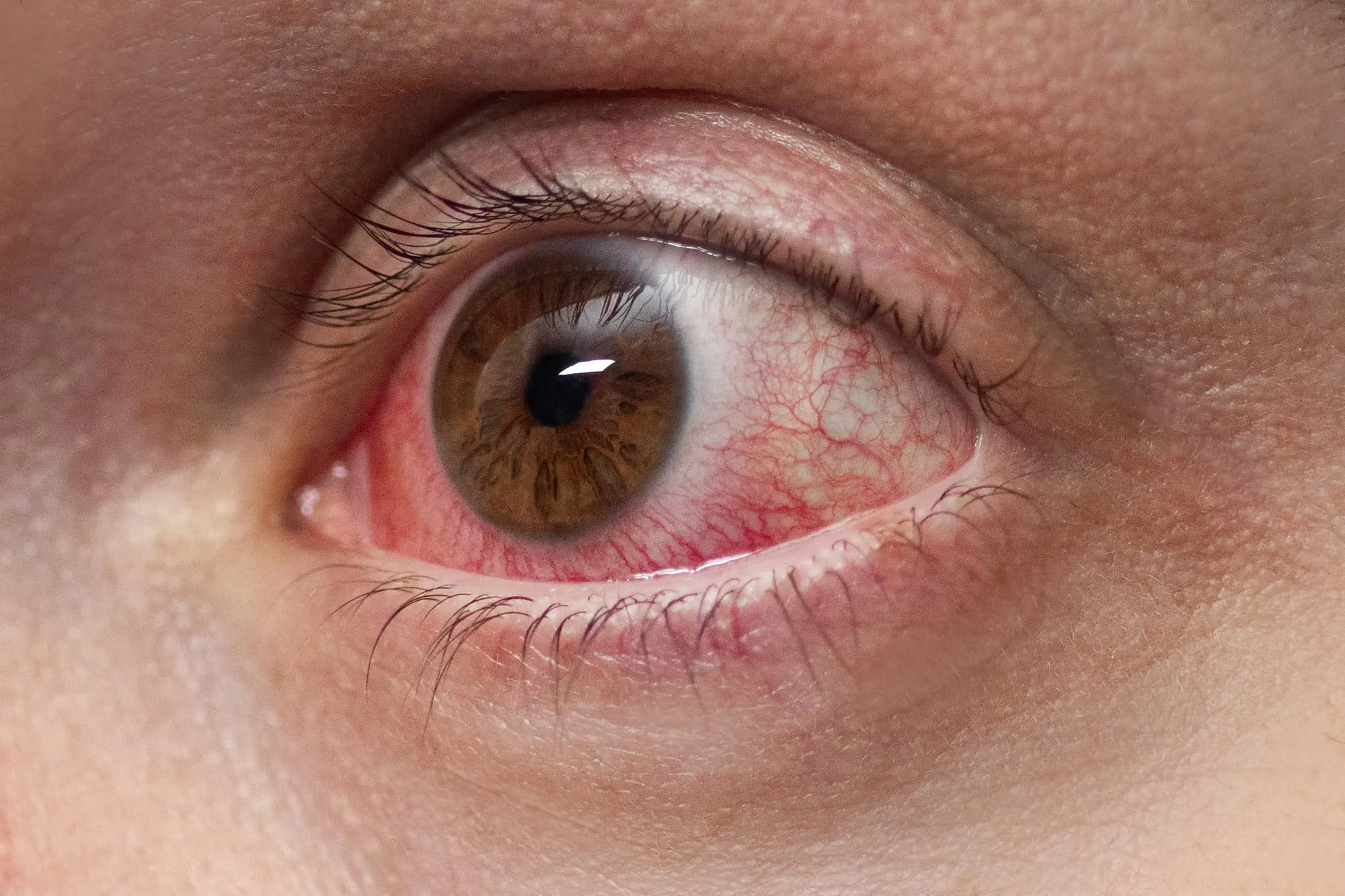
What are the symptoms of ocular rosacea?
The symptoms of the eye can be confused with those of a allergic conjunctivitis o visual fatigueTearing, itching, redness of the eye, blurring of vision at certain times (due to tearing).
Eczema may or may not be visible on the skin, although it is common for the patient to feel discomfort as well.
Inflammation caused by rosacea in these structures (eyelid skin and conjunctiva) increases the risk of infections such as conjunctivitis, sties or blepharitis. chalazion.
What are the causes of this disease?
We are not clear about the causes of this problem, or rather, we know that it is not unique. Some clinical studies seem to reinforce the hypothesis of the existence of a certain genetic predisposition in patients with several cases within their immediate family. It is sometimes transmitted from parents to children, but it is not an autosomal dominant gene.
In other cases, ocular rosacea is environmental, but the factors may vary from patient to patient. In some cases, there is a tolerance threshold. For example, if environmental pollution negatively influences a patient's case, they are likely to feel worse when there are a lot of solid particles in suspension due to the absence of rainfall. If another patient is allergic to pollen, he or she will feel worse in spring, despite the existence of summer-flowering species.
Let's take a look at this list of possible environmental agents responsible for rosacea, when it affects the conjunctiva or eyelid skin:
- An unbalanced diet or one very rich in spices, salt, caffeine...
- Alcohol or tobacco use.
- Sweating due to very hot weather or certain sports.
- Stress and anxiety, especially if prolonged over time.
Treatments for ocular rosacea
Antibiotics and corticosteroids in severe cases
If the crisis, which usually lasts between 1 and 3 weeks, has allowed a bacterial infection to develop, we prescribe antibiotic treatment in the form of eye drops or ointment for the periocular area as a first step.
If the episode is very intense and bothersome, we assess the advisability of prescribing corticosteroids also for the first few days.
Hygiene
This is the main point when we discuss how to treat ocular rosacea. The patient needs to take care of the eyelid hygieneusing only suitable products: non-irritating and non-occlusive. For this reason, it is always better to consult an ophthalmologist rather than a dermatologist alone.
If there is usually redness in the eye, the ophthalmologist will establish the causes and prescribe a treatment to be followed at all times or only if the symptoms worsen. This can be as simple as the use of artificial tears, or the application of antihistamines in difficult times, due to the presence of allergens or stress.
There may also be skin and eye hygiene products reserved for these periods where the risk of acute episodes is higher.
Lifestyle changes
Of course, it is in the patient's best interest to abandon, or at least reduce, these habits that can make symptoms worse.
To find out which ones are affected, we need to cut them out completely for a while, see how they evolve and, if necessary, try to reintroduce them carefully, observing if any changes occur.
IPL
The pulsed light therapy Intense may also improve the symptoms of rosacea, as it helps to restore the function of the Meibomian glands, which are in the eyelids and are affected in this condition.
Ocular rosacea affects the eyelids and conjunctiva, although symptoms may be seen in only one or both. Related to a non-determinant hereditary component, it is worsened by a series of environmental factors. If the episodes or crises and their complications are not treated, it could end up affecting vision with unfavourable prognoses. For this reason, and for the patient's quality of life, we insist that they adopt a series of habits to reduce and space out these outbreaks.